



In general, when permanent teeth begin to emerge from the gingiva, the roots of deciduous teeth start to absorb and gradually loosen, eventually falling out until the permanent teeth completely take their place. If deciduous teeth do not naturally fall out while permanent teeth have already grown in, this condition is known as "retained deciduous teeth" or "persistent deciduous teeth."
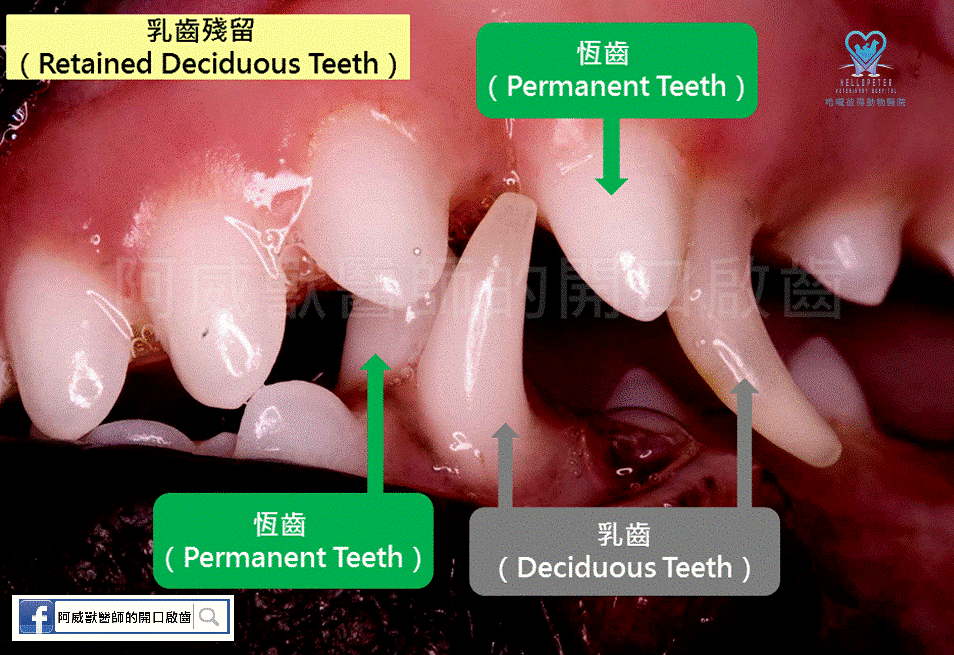
Persistent Deciduous Teeth (PDT) are more commonly observed in small and miniature dog breeds, while being less frequent in medium to large-sized dogs. However, it can occur in cats of any breed.
There are various possible reasons for the persistence of deciduous teeth. The most widely accepted theory suggests that when permanent teeth deviate from their normal growth direction, the reabsorption of deciduous teeth may not occur, resulting in the coexistence of deciduous and permanent teeth in the same location. Another perspective suggests that the retention of deciduous teeth may cause abnormal growth directions of permanent teeth, leading to impaction and ankylosis. Differential diagnoses in clinical settings may include supernumerary teeth and malformed crowns.
The occurrence of persistent deciduous teeth is more common in dogs, though it is not impossible in cats (cases have been reported). It typically happens bilaterally and may lead to traumatic pulpitis, facilitate calculus formation, contribute to periodontal disease, and cause malocclusion.
Once PDT is identified in animals, prompt extraction is crucial. Failure to remove retained teeth may lead to inflammation and infection in the affected area, continuing to impact occlusion. Complete extraction is necessary to avoid harm to the permanent teeth.
Due to the fragility of deciduous teeth and the associated problems of reabsorption and ankylosis, tooth extraction can be challenging. Veterinarians commonly employ two techniques: open extraction, which ensures thorough removal but results in a larger incision, and closed extraction, which is less invasive but carries a higher risk of root fracture and retention in the alveolar bone. Our hospital utilizes ultrasonic bone scalers for extractions, minimizing damage to periodontal tissues and reducing the risk of root fracture.
For animals with persistent deciduous teeth, thorough evaluation by a veterinary dentist is essential to determine the appropriate extraction method. Owners should not overlook the importance of addressing this issue promptly.
【Veterinary Dentistry | Glossary】
Impaction: Abnormal eruption position of a tooth, often due to crowding in the dental arch or pathological changes in the dental sac (such as cysts). It may lead to malocclusion, infection, pain, or nerve paralysis, but it can also be asymptomatic. Diagnosis often requires dental X-rays, as clinical examination may not reveal non-erupted teeth. Wisdom teeth in humans commonly become impacted due to misalignment during growth. Early removal of impacted teeth is recommended, as delayed removal increases difficulty and the risk of postoperative infection.
Ankylosis: The fusion of tooth root dentin or cementum with the surrounding alveolar bone, eliminating the normal space for periodontal ligaments. The extraction or correction of ankylosed teeth is challenging, possibly requiring surgery and causing significant damage to surrounding tissues. Poor treatment outcomes may affect adjacent normal teeth.
Supernumerary Teeth: A developmental anomaly where the number of teeth in the dental arch exceeds the normal count. Supernumerary teeth can occur in both deciduous and permanent dentition, and their shape, position, and growth direction can vary widely. They may lead to impaction, delayed eruption of permanent teeth, malocclusion, resorption of adjacent tooth roots, and the formation of follicular cysts. Malformed Crown: Also known as gemini or twinning teeth, this is a developmental abnormality where one tooth splits into two distinct teeth with a common root or root canal. The morphology typically involves two tooth crowns of varying sizes.
HelloPeter Veterinary Hospital
Phone: +886-4-2472-8828
Official Website: www.hellopeter.com.tw
Hospital Hours: Monday to Friday 10:00~20:00 (by appointment only), 12:00 to the end of all appointments on Saturday, Closed on Sunday
#乳齒殘留 #RetainedDeciduousTeeth #阻生齒 #Impaction #牙骨沾黏 #Ankylosis #贅生齒#SupernumeraryTeeth #畸形冠 #MalformedCrown
#哈囉彼得動物醫院 #陳重威獸醫師 #口炎貓口腔治療研究計畫 #動物牙科推薦 #動物口腔外科 #MGRS #牙齦黏膜置換手術 #貓 #口炎 #cat #台中獸醫院 #寵物牙科推薦 #台中動物醫院推薦 #口炎貓 #高雄醫學大學
#阿威獸醫師的開口啟齒 #狗貓兔牙科 #狗貓兔口腔外科 #口腔衛生 #牙科X光 #超音波骨刀機 #口鼻廔管 #GTR #動物植牙 #GBR #拔牙 #口水 #3d列印動物牙套