【Severe periodontal disease causing squamous cell carcinoma in a Maltese dog's oral cavity.】
Our patient, Annie, is an 8-year-old spayed female Maltese dog. Annie suffers from severe periodontal disease, leading to tooth loss, gingival recession, and alveolar bone loss. The owner brought Annie to our hospital for dental scaling and periodontal treatment. During the treatment, a mass was found between the right maxillary incisor and canine (103~104) of the dog. Considering the poor oral health might lead to oral tumor formation, the owner was advised to have the growth undergo histopathological examination.
The examination revealed the growth in Annie's oral cavity to be squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), one of the most common oral malignant tumors in dogs. Since Annie's tumor was classified as a low-risk Grade 1 (G1) and showed no invasion into surrounding normal tissues, extensive maxillofacial surgery was not performed subsequently. However, the owner was reminded to schedule regular follow-up visits to ensure the tumor did not recur and to brush Annie's teeth daily to maintain good oral hygiene.
Poor oral hygiene can lead to oral cancer; you can refer to Dr. Chung-Wei Chen's article in our hospital:
https://www.hellopeter.com.tw/content-142.html
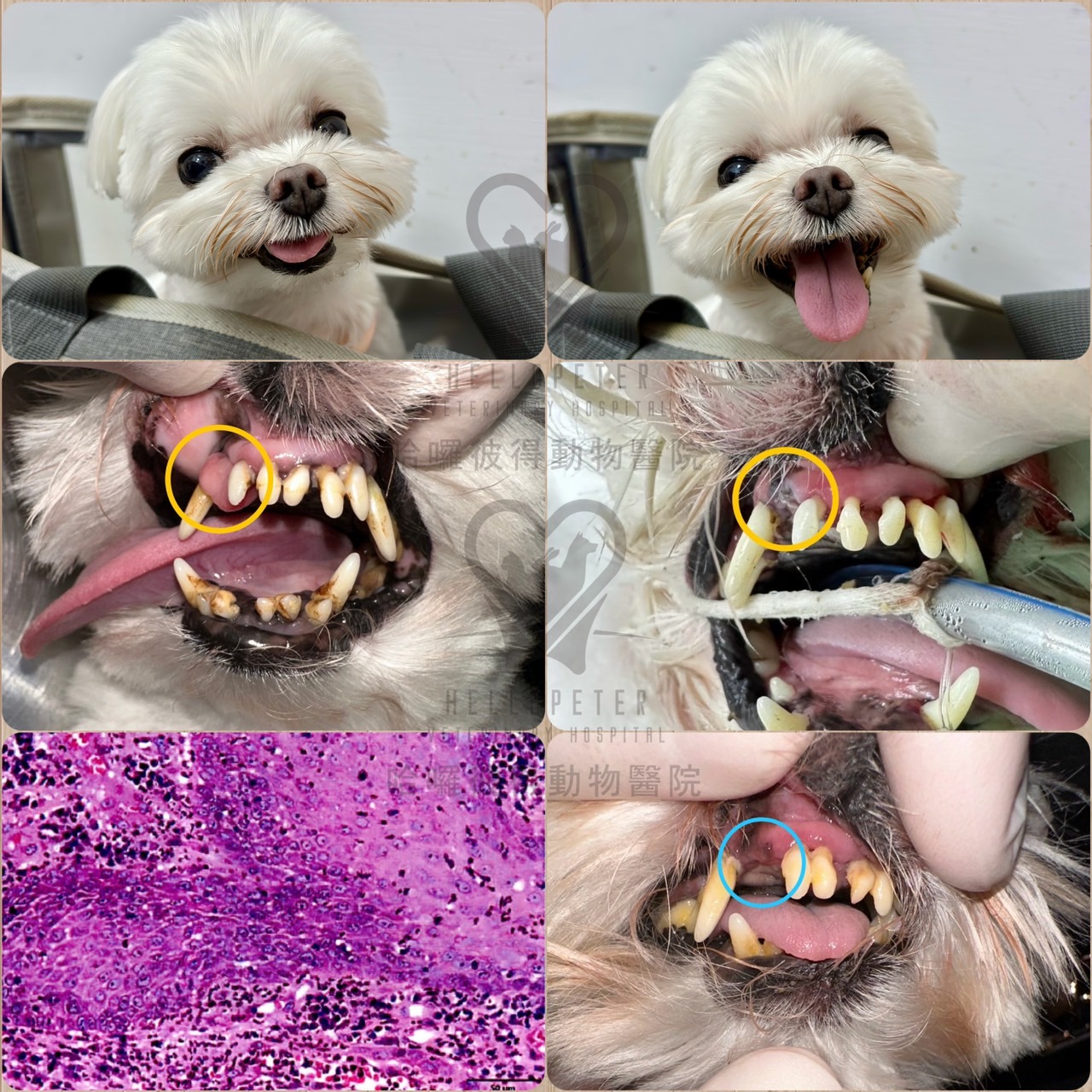
In this case, Annie was fortunate to have the tumor detected early, at Grade 1 (G), and the location of the tumor in the anterior maxilla usually has a better prognosis than tumors in the posterior oral cavity. Therefore, extensive excision of healthy tissue around the tumor was unnecessary. Post-operative healing was also excellent.
Seven months after surgery, Annie, the Maltese dog, returned for a check-up. The gum at the site of tumor removal healed normally, and no new growths were observed. The owner was pleased that extensive excision was not required. We will continue to monitor Annie to ensure the maintenance of her oral health.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the most common oral cancer in dogs and cats, with cats having the highest incidence, accounting for 64-75% of all oral cancer cases, and dogs accounting for 24-30% of oral cancer cases, second only to malignant melanoma (approximately 30-40%). It is one of the common oral malignant tumors seen in clinical practice.
Although SCC has a low metastatic rate, it exhibits significant invasiveness to surrounding tissues, potentially damaging gingiva, oral mucosa, tongue, tonsils, alveolar bone, and teeth, and may even cause pathological fractures. Therefore, surgical treatment usually involves extensive excision (at least 1.5-3 cm of normal tissue around the tumor), including removal of underlying bone, and may require concurrent chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc., to ensure thorough tumor removal (Niemiec et al., 2020, Reference 2). The surgical course of treating the tumor may cause significant damage to facial structures, and subsequent facial reconstruction surgery is also a major undertaking, posing a significant burden on the pet's body and owner's care.
Due to the tendency of oral cancer cells to metastasize and invade surrounding tissues, treatment with chemotherapy or radiotherapy alone yields poor results; surgical excision is essential.
The grading of SCC is as follows (National Cancer Institute (NCI), 2021, Reference 1):
Grade X (Gx): Grade cannot be assessed (undetermined grade)
Grade 1 (G1): Well differentiated (low grade)
Grade 2 (G2): Moderately differentiated (intermediate grade)
Grade 3 (G3): Poorly differentiated (high grade)
Grade 4 (G4): Undifferentiated (high grade)
A higher grade indicates poorer tumor differentiation, increased malignancy, and a higher probability of metastasis to other organs, resulting in poorer treatment outcomes.
Owners can observe if their dogs or cats experience such as increased drooling, difficulty swallowing, weight loss, oral bleeding, etc. If so, prompt medical examination is recommended for early detection and treatment.
For more cases of successful dental and oral surgery treatments in our hospital, please refer to:
https://www.hellopeter.com.tw/contents-2.html
#
squamouscellcarcinoma #
SCC #
malignantmelanoma
#
tumour
#
鱗狀上皮細胞癌 #
黑色素腫瘤 #
狗 #
dog #
Maltese #
瑪爾濟斯犬#
口腔 #
惡性腫瘤 #
口腔癌
#
陳重威獸醫師 #
DrChungWeiChen #
DrRichardChen #
牙科獸醫推薦
#
哈囉彼得動物醫院 #
牙科獸醫 #
台灣牙科獸醫 #
HellPeterVeterinaryHospital #
動物牙科推薦 #
寵物牙科推薦 #
dog
#
動物口腔外科 #
獸醫牙科 #
pet



